The Advent of the Flexible Electronics Market

As the next era of electronic products emphasizes more into the physical features such as flexibility, thinness, and lightweight, companies are looking for more effective methodologies to mass produce these components. In terms of electronic visibility features, the emphasis is placed upon high clarity, anti-reflection, anti-fingerprint and anti-glare. In terms of durability, the emphasis is placed upon temperature resistance, scratch resistance, and toughness.
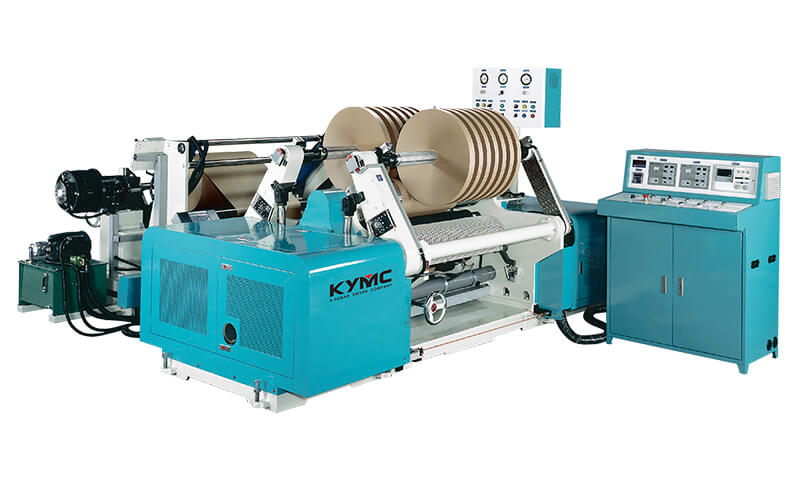
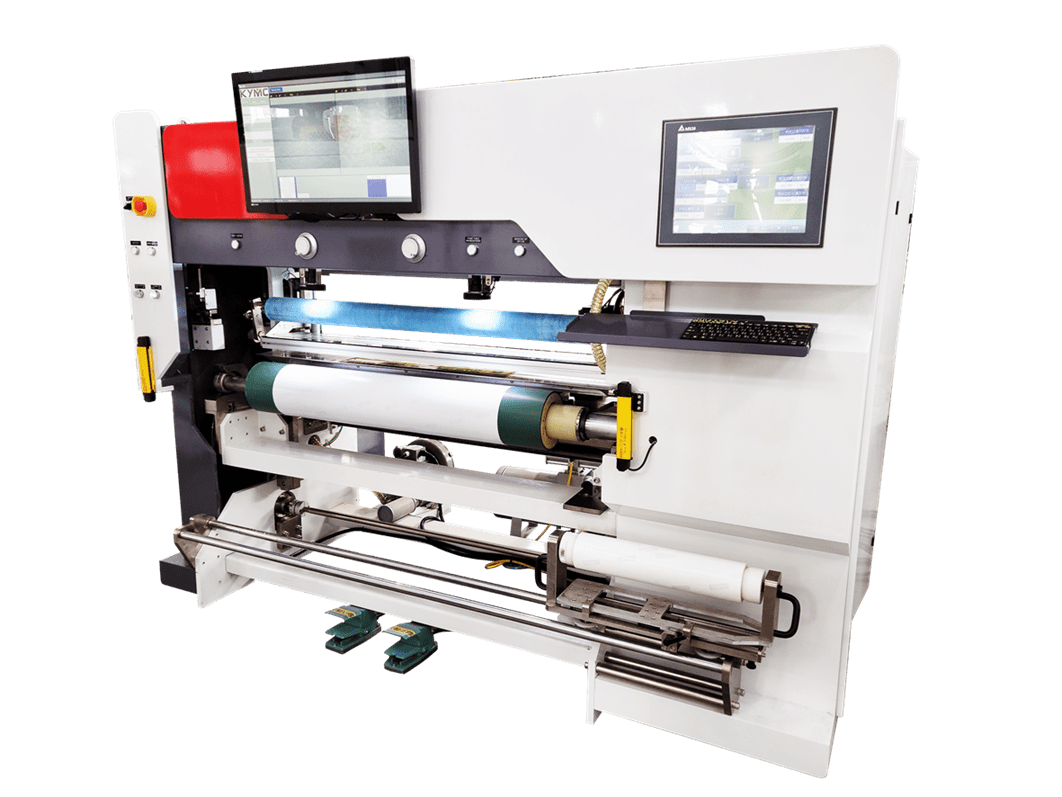
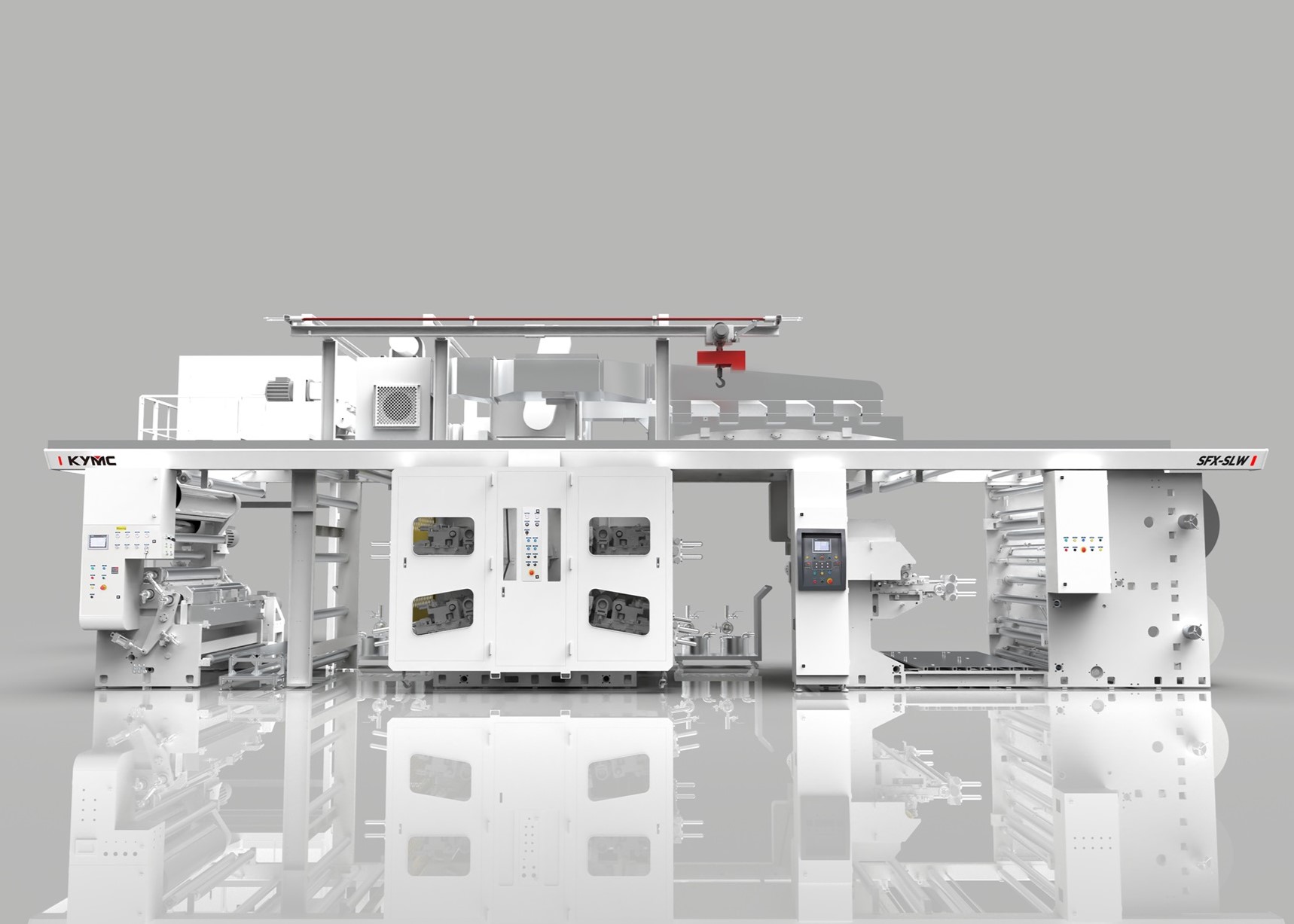
There are many manufacturing processes such as debonding and laser direct writing. At KYMC, as a printing press manufacturer, we print it. At KYMC we have developed presses to print conductive ink and dielectric ink onto substrates. The benefit of direct printing is a low cost and more environmentally friendly manufacturing method. According to IDTechEx the printed flexible electronic sector is set to reach over $73 billion by 2025.
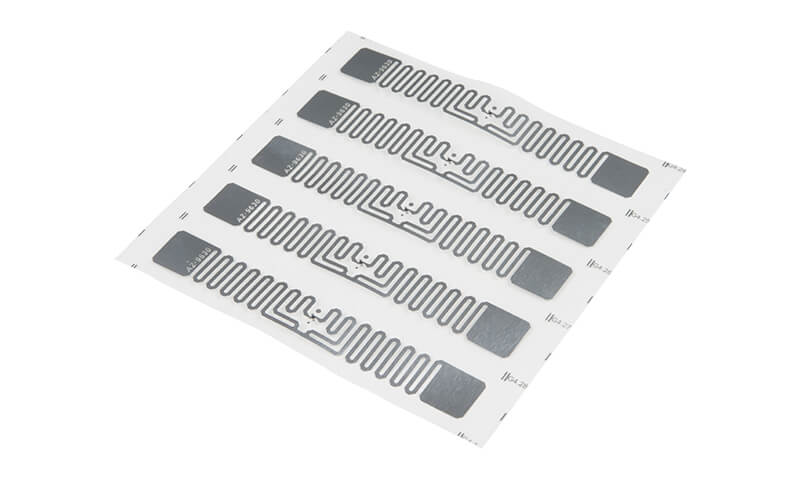
The industry application for printed flexible electronic spans across many sectors. Sectors including automotive, logistics, wearable devices, healthcare, commercial display, consumer electronics, gaming, education, and packaging. These sectors have adopted the printing methodologies to develop HF & UHF RFID tags, functional substrates, flexible OLED lighting, flexible HMI panels and flexible sensors.
Take the automotive as an example. The taillight of cars is becoming more and more fashionable. The different shapes and designs are made possible with the adoption of flexible OLED lights. No other light source offers such enormous freedom of designs as OLEDs thanks to their ultra-thin and flexible construction. Printed sensors have been inserted into vehicle seats for some time now to register whether the seat is occupied or not. If required, heating is provided to the seats when the seats are occupied.
In the packaging industry sensors could be applied to transmit information regarding when the packaging has been opened. RFID tags could be attached for logistics tracking. RFID provides an easy way to insert or read information throughout the supply chain. RFID is a much more efficient way for tracking as multiple tags can be scanned simultaneously without having to visually see the RFID tags. When compared to barcodes, where each scanning can only to be done one at a time and can only be completed when the barcode is visible.
Article by Daywey Chen, KYMC