Polyethylene (PE) Extrusion Paper Coating V.S Water Based Paper Coating

Paper products are used throughout our daily life to contain food and drinks. This include paper cup, paper bowl, wrap paper and disposable tableware. The reason that these paper containers are able to prevent the liquid and grease from leaking out is that they are coated. Today, most paper containers are Polyethylene (PE) coated. PE coating is not biodegradable or compostable. Even though PE coated paper are recyclable, the recycling processes are time consuming and labor intensive, resulting in most PE coated paper to end up in landfills. According to BBC news, 99.75% of paper coffee cups are not recycled. According to Footprint Media Group, just 6% of paper cups are being recycled. Whatever, the actual recycling rate is, one thing is certain, it is low.
What makes PE coated paper so popular?
If PE coated paper are non-recyclable from a cost perspective and causing environmental burden, why are PE coated paper still being adopted at a mass scale?
Some of the characteristics of PE coated paper that make them so popular include:
A simple and a low-cost solution
PE can be coated onto the paper easily. The coating attached to the paper will not strip away easily. The process can be completed without any chemical solvent’s assistance, making it simple and cost effective.
Liquid, water and grease resistance
PE coated paper are excellent choice for food and drink containers due to their liquid, water and grease resistance properties. They perform much better when compared to wax paper. Coated paper provide a near 100% resistance property.
Heat sealable
By applying heat, the PE coating can be remelted on the coated paper and reach a sealing purpose.
Tear resistance
A PE coated paper are much more tear resistant. At the same time providing stiffness to the paper to make them more robust in their structure and prone to wrinkles.
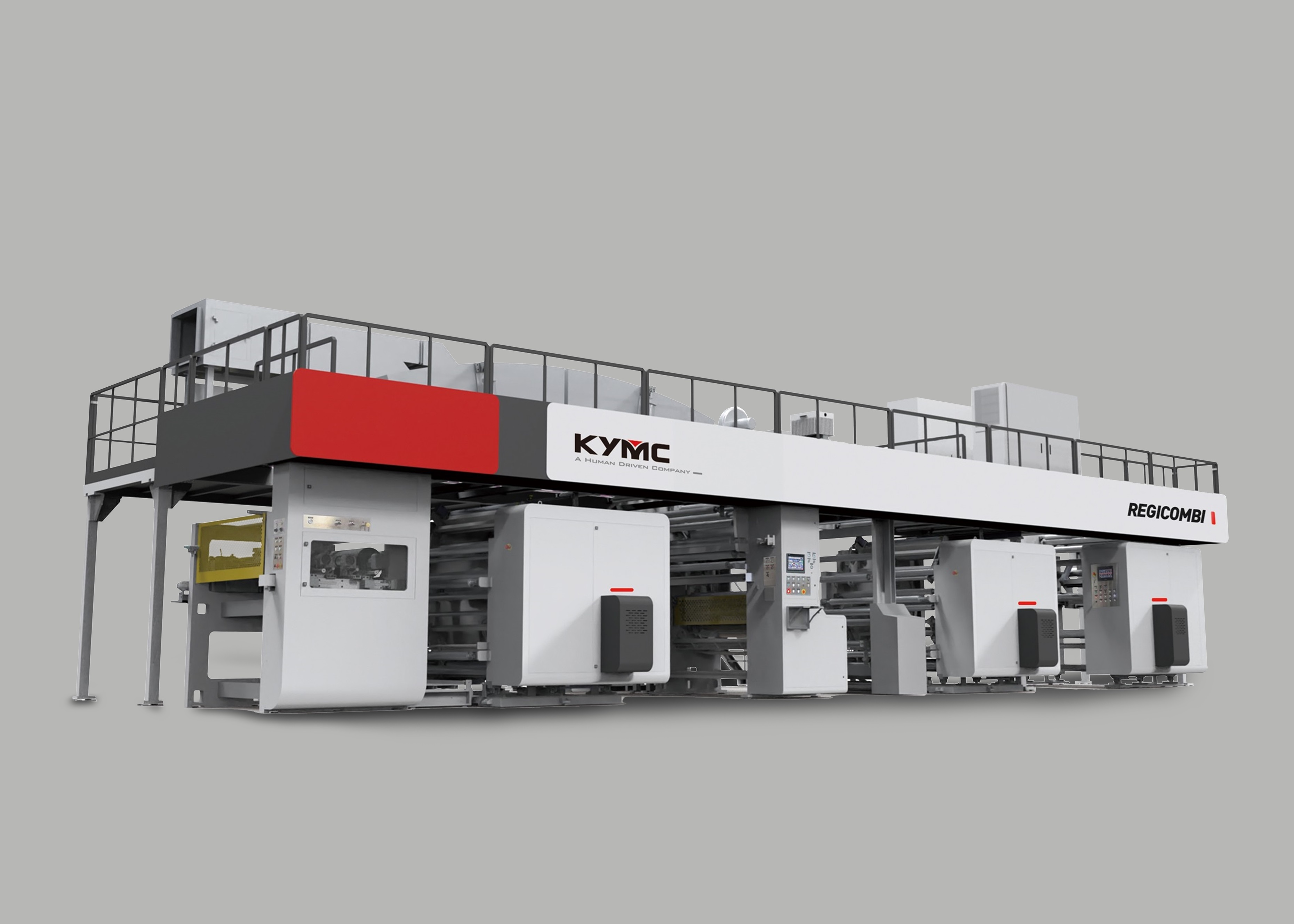
PE coated paper production
PE coated paper are commonly produced through the extrusion coating process, where PE are melted under heat and pressure in an extruder, then extruded through a slot die as a thin web where they are drawn down onto the paper. Depending on the usage requirement the quantitative amount of PE coating used on paper are generally between 8 gsm to 20 gsm. If the application is for waterproof and moisture proof packaging, then 8-10 gsm of PE coating will suffice. If the application is for gluing the PE coated paper to other materials, then usually 12-16 gsm of PE coating is applied. Lastly, if the goal is to produce paper containers that can be heat-sealed, then 18-20 gsm of PE coating should be applied.
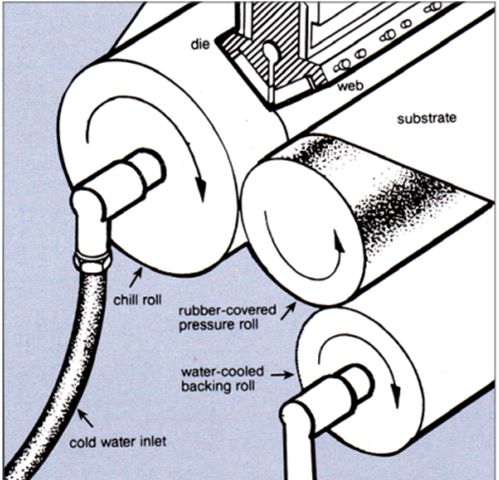
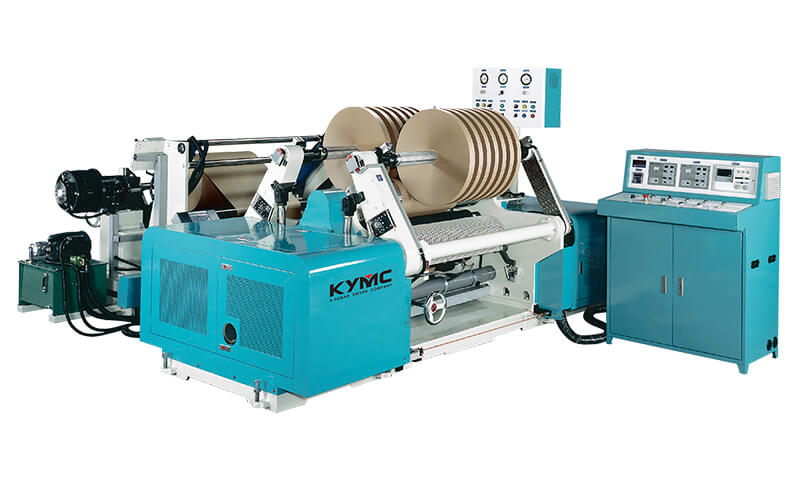
Extrusion Coater
Source:http://www.qenos.com
TALK TO A KYMC REPRESENTATIVE
What are the PE coated paper substitutes?
As the market becomes more environmentally conscious, more environmentally friendly solutions have been developed to replace the long-standing PE coated paper. Instead of PE, water-based coating substitutes are promoted. The aim of these water-based coatings are to maintain the functionalities of the PE coating while taking away the non-environmental friendly characteristics such as hard to separate from paper fibers, non-biodegradable and non-compostable.
Water-based coated paper production
Reverse roll coating is a suitable process for water-based paper coating. Different types of coating applications, different paper weights and different paper types will require different coating weights. Reverse roll coater can provide a large range of coating weight laydown(10~150gsm wet). To be able to work with coating liquid of various viscosity from 150cps to 20,000cps. The flexibility of the reverse roll coater in providing a wide range of coating weight laydown and the ability to work with a wide range of viscosity makes it the go-to coating process when it comes to water-based paper coating.

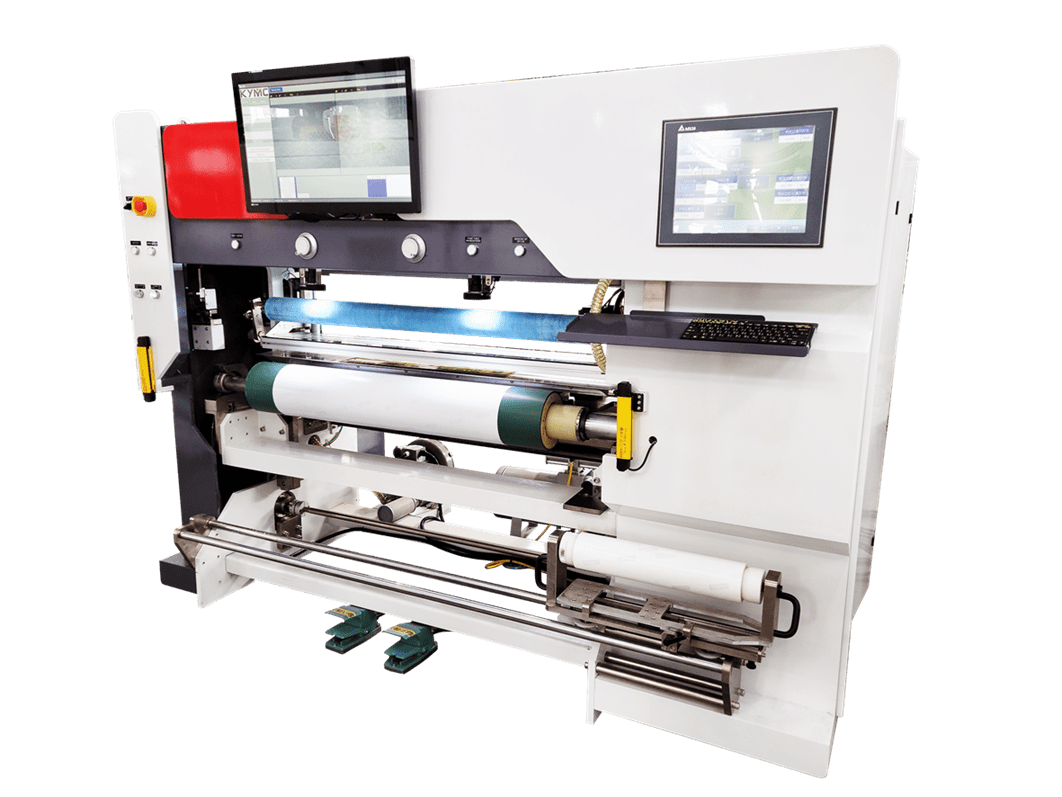
KYMC reverse roll coater
Drying
There are many drying processes. This includes gas convection drying through heated gases, conduction drying through the heated drum, plate or warm/hot-air flow and infrared drying via MIR, KIR or NIR. Different drying processes have their own advantages. When it comes to drying water-based coating solutions and paper that are heat sensitive, NIR drying would be a good choice. NIR stands for Near Infrared drying, it adopts wavelength in the range of 800nm up to 1,200nm with a peak of 800nm. In this range it incorporates the highest possible energy densities in the smallest applicable areas without affecting substrates and the surrounding environment. The NIR radiation can penetrate directly into the depth of the coating body to remove the water. As for convection and conduction technologies, the energy is absorbed at the surface and is then slowly conducted into the coating. In summary, NIR is a much faster way and much more energy efficient way of drying water-based solutions. Experiments have been conducted (wet application weight 250gsm; dry weight 125gsm) to compare gas drying with NIR drying. The experiment showed the gas drying consumed 220-370kwh/1000m².
Source:
https://jirongpacking.com/pe-coated-paper/
https://www.yanxiyan.com/pe-coating-paper/
http://www.qenos.com/internet/home.nsf/(LUImages)/TG4Exco/$File/TG4Exco.pdf
https://www.foodonline.com/doc/new-paper-coating-technology-offers-alternati-0001

Article by Daywey Chen, KYMC